Introduction
Mountains are important for understanding Geography. They contribute to the development of Climate, Water Systems, The Origin of Rivers, and Biodiversity as well as contribute to the spread of Deserts. Mountains create landforms, and “MOUNTAINS” are an important part of Physical Geography and Prelims Map Work for UPSC aspirants and Mains Physical Geography/Social studies.
Recently, the Supreme Court of India (Court), which has jurisdiction over the country, directed that the Government of India (Centre) should prepare a Management Plan for Sustainable Mining (MPSM) of the Aravalli Range, one of the oldest fold mountains in the world.
Note: To understand the role of gender in citizenship rights, you can read more about the feminist concept of citizenship
Overview of Supreme Court’s Direction
In its decision, the Court defined the Aravalli Hill as any landform greater than 100 meters and the Aravalli Range as any cluster of hills located within 500 meters of one another. T
The Court also directed that all new or renewed mining leases in Aravalli State would be stopped until the Centre prepares a Management Plan for Sustainable Mining. Therefore, this plan will be prepared by the C.E.C. with assistance from the India Council for Forestry Research and Education (ICFRE) and will identify those areas of the Aravalli Range that are suitable for mining, as well as all ecological no-mining zones, and restoration and conservation zones.
The judgement emphasises the importance of mountain systems for India’s ecological health and why the Conflict of Interest Study has added an increasing number of questions related to geomorphology, environmental protection and map skills. In order for reviewers to get a sense of how far along we are in terms of geomorphology and other related fields, one should study the best geomorphic materials used today.
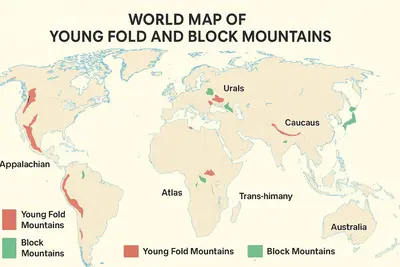
What Are Young Fold Mountains?
Young Fold Mountains are mountains that develop as a result of two tectonic plates colliding and the Earth’s crust folding in upon itself. Think of it like how a rug would look if it were pushed from both ends and folded up.
Characteristics of Young Fold Mountains
- Young Fold Mountains are young (millions of year old).
- They are characterized by high rugged peaks with steep slopes.
- Young Fold Mountains are often tectonically active.
- Young Fold Mountains are located at converging tectonic plate boundaries.
- Examples of Young Fold Mountains: the Himalayas, Andes, Rockies, Alps.
List of Young Fold Mountains
A. North America
- Alaskan Range – Alaska, USA
- Brooks Range – Alaska (USA) & Yukon (Canada)
- Rocky Mountains – Canada & USA
- Appalachian Mountains – Eastern USA
(Geologically older but still formed by folding → kept under fold mountains)
B. South America
- Andes Cordillera – Venezuela, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia, Chile, Argentina
C. Southeast & South Asia
- Arakan Yoma / Chin Hills – Myanmar & India (near Mizoram)
- Pegu Yoma – Myanmar
- North-Eastern Hills – Nagaland, Manipur, Mizoram, Tripura, Meghalaya (India)
- Himalayas – India, Nepal, Bhutan, China, Pakistan
- Trans-Himalayas – Tibet, Ladakh, Karakoram
D. Central & West Asia
- Hindu Kush – Afghanistan, Pakistan
- Sulaiman Range – Pakistan
- Elburz Mountains – Northern Iran
- Taurus Mountains – Turkey (towards Mediterranean Sea)
- Pontic Mountains – Turkey (towards Black Sea)
E. East Asia
- Japanese Alps – Japan
F. Europe & Eurasia
- Caucasus Mountains – Russia, Georgia, Azerbaijan
- Alps – Switzerland, France, Austria, Italy, Germany, Monaco, Slovenia
- Carpathians – Romania, Ukraine, Slovakia, Poland
- Pyrenees – France & Spain
- Dinaric Alps – Croatia, Bosnia & Herzegovina
G. Oceania
- Great Dividing Range – Eastern Australia
- Southern Alps – South Island, New Zealand
H. Africa
- Atlas Mountains – Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia
- Anti-Atlas Mountains – Morocco
I. Eastern Europe / Eurasia Boundary
- Ural Mountains – Russia
What Are Block Mountains?
Block Mountains are mountains created by the displacement of blocks of the Earth’s crust, caused by faulting; when a fault forms, some blocks of land are displaced upward and some blocks are displaced downward.
Characteristics of Block Mountains
- They are formed by vertical movement of the Earth’s crust (from faulting).
- They have steep, linear sides.
- Block Mountains are formed in regions of faulting.
- Examples of Block Mountains: Black Forest Mountains, Vosges Mountains, Vindhya Mountains, Satpura Mountains.
List of Block Mountains
Europe
- Vosges – Northeastern France
- Black Forest – Southwestern Germany
India
- Vindhya Range – Central India
- Satpura Range – Madhya Pradesh & Maharashtra
Map Practice for the UPSC Exam
The following is the correct way to practice marking mountains on a blank world map:
- Mark mountaintops of only five to seven selected mountain chains per day. You must sharpen your skills by marking your previous day’s blank information.
- Repeat 7 simple maps (one from each region) in no longer than 10 minutes after completion.
Instructions
- Mark mountains based upon continents only: First mark mountains in Asia, Africa, Europe, The Americas, and The Pacific Ocean.
- Mark mountain ranges as lines not dots; e.g., Rockies, Andes, Himalayas.
- Indicate only the tallest mountain of every continent (Everest, Denali, Kilimanjaro, etc.) on a world map.
- Indicate with arrows the direction of traversal (e.g., Andes (North-South).
- Utilize 3 different color codes.
- Blue=Old mountains; Red=Young fold mountains; Green=Plateaus/Block Mountains.
- Place this map on a wall and review before sleep each night.
Smart Grouping Techniques (Easiest)
1.Use vertical (North-South) mountain pairs.
- Rocky Mountains and North America.
- Andes Mountains and South America.
- Think of these as twin vertical supports on the left side of North and South America.
2. Use the horizontal mountain chain of Europe.
Alps, Carpathians, Dinaric Alps.
To remember: make a smile on a horizontal plane from Switzerland to the Balkans. This is the “smiling mountain belt” of Europe.
3. Africa has two paired Mountains.
Atlas and Anti-Atlas.
To visualize: Africa’s northwest has these two mountains as “double hats.”
4. For Asia, it has 3 major mountain ranges.
Use this easy method: H-T-S.
- Himalaya=highest
- Tianshan=China and Kyrgyzstan; and
- Sayan = Russia and Mongolia.
To remember: “H-T-S = High Tall Mountain Systems.”
5. Australia has a Great Dividing Range.
Use it as a spine.
Quick Memory Hacks & Patterns.
- “Young Edge Rule”.
Young Fold Mountains typically occur on the edges of continents. Examples: Himalayas, Andes, Rocky Mountains, and Alps.
- “Tallest in the Middle of Asia”.
An example of this is the Himalayas, resulting from the collision of the Indian subcontinent with Euraisia.
- “The Americas = Two Long Ceilings”.
The left side (Wall) consists of: Rocky Mountains and Andes.
The right side= Mostly plains
- Africa’s main landform is flat, apart from the minor mountainous regions in the northwest (Atlas) and east (Ethiopian Highlands).
- Australia has not many mountains due to its location as the 3rd continent in the south-east of the planet.
Differences Between Young Fold Mountains & Block Mountains
| Feature | Young Fold Mountains | Block Mountains |
|---|---|---|
| Age | Geologically young | Geologically old |
| Formation | Formed by folding of sedimentary rocks due to plate collision | Formed due to faulting → uplifted blocks (horsts) & lowered blocks (grabens) |
| Structure | High, steep, sharp peaks | Flat-topped, steep-sided |
| Examples | Himalayas, Andes, Rockies, Alps | Vosges (France), Black Forest (Germany), Sierra Nevada (USA) |
| UPSC Relevance | Frequently asked in map questions, geomorphology basics | Important for understanding landforms & rift valley PYQs |
UPSC Prelims PYQs on Mountains & Map-Based Geography
1. Questions on Mountain Ranges (India & World)
1.1 Ordering / North–South / East–West Arrangements
2020– Arrange the following in North–South direction:
- Himalayas
- Narmada Valley
- Satpura Range
- Vindhya Range
2018– Arrange the following in East–West direction:
- Himalayas
- Aravallis
- Vindhyas
- Satpuras
2014– Arrange the following mountain passes in North–South order:
- Nathu La
- Jelep La
- Bomdi La
2013– Arrange the following in North → South order:
- Karakoram
- Zanskar
- Pir Panjal
- Shiwalik
1.2 Questions on Features of Specific Mountain Ranges
2023– Which of the following are characteristics of the Himalayas?
- Recent origin
- Fold mountains
- Orogenic activity
- Presence of deep valleys
2021– The Naga, Khasi & Garo hills are part of: Himalayas / Purvanchal / Peninsular Block?
2017– The Alps, Andes, and Himalayas belong to which type of mountains? (Young Fold Mountains)
2016– The Great Dividing Range is located in which continent? (Australia)
2015– The Atlas Mountains are located in which region? (Northwest Africa)
2012– Which of the following are Block Mountains?
- Vosges
- Black Forest
- Sierra Nevada
2. PYQs on Peaks (Highest Peaks / Locations)
2.1 India
UPSC 2015– Where is Mt. Satopanth located?
- Uttarakhand / Himachal Pradesh?
UPSC 2013– Which of the following is the highest peak in south India?
- Anaimudi
2.2 World
- UPSC 2018– The Kilimanjaro Mountain is located in: Tanzania
- UPSC 2016– Mount Elbrus is located in: Russia (Europe)
- UPSC 2015– Mount McKinley / Denali belongs to: North America
Conclusion
- Continents and highest mountains that can be found: The two major mountain ranges found in the Americas are the Rocky Mountains (North) and the Andes Mountains (South).
- Europe’s smile is shown in the sequence of mountains starting with the Alps and followed by the Carpathians and then the Dinaric Range.
- Africa has a “double” cap with the Atlas Mountains to the north and the Anti-Atlas Mountains to the south.
- In Asia, the H-T-S trio of mountains are found. Again, in Australia, only small mountains can be found.
Memorizing the location of Mountains
In UPSC examinations, candidates will be asked to identify all of the following:
- Matching mountain ranges with a given continent
- Arranging mountain ranges in North-South sequences
- Identifying mountain belts using physical maps of the continents
- Identifying and linking mountain ranges to their specific countries/continents
The last effective memorization technique is to prepare a “one-page” world map of the entire globe and to review it for approximately 2 minutes each day. If you follow this technique for a period of 30 days, you will be able to recall all the mountain ranges without any additional effort.

